Projects
Our In-Progress and Completed Projects
The Plant Health Centre funds projects to understand current and future threats, risks, and management strategies in maintaining plant health across sectors in Scotland.
The projects listed below are 'in progress' or 'completed'.
Reports from completed projects can be searched here
There are 66 projects listed below.
Supporting Community Farm Biosecurity
Lead Author: Emma Brierley
Plant waste management knowledge exchange
Lead Author: Matt Elliot
Plant Health Fellowship
Lead Author: Ruth Mitchell
Groundkeeper mapping for PCN control
Lead Author: Jim Wilson
Expansion of PHC online Plant Health Resource
Lead Author: Katy Hayden
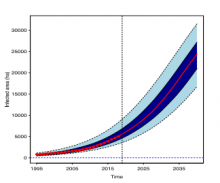
The future threat of PCN in Scotland
Lead Author: Vivian Blok